Every year, many have been afflicted by rabies globally where most have been chomped by a rabid dog. With the obtainability of vaccines for both humans and animals, it resulted to a decrease in the cases of rabies in developed countries.
Rabies is caused by a virus that affects the central nervous system which leads to inflammation of the brain. Domestic cats, dogs and rabbits as well as wild animals such as raccoons, skunks and bats can transfer the virus to humans through scratches and bites. The objective in dealing with the virus is rapid response.
What are the indications of rabies?
The incubation period usually takes 4-12 weeks for an individual to develop the symptoms of rabies once infected. Nevertheless, the incubation period can range from a few days up to 6 years.
The initial start of rabies is marked by flu-like symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Tingling sensation
- Muscle weakness
Aside from these initial symptoms, there is also a burning sensation at the bite site. As the virus continues to attack the central nervous system, there are 2 various types of disease that can develop.
Furious rabies
An infected individual who develops this type is hyperactive and excitable along with erratic behavior. The other symptoms include the following:
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Agitation
- Confusion
- Excessive salivation
- Hallucinations
- Fear of water
- Difficulty swallowing
Paralytic rabies
This type of rabies takes a longer time to set in but has severe effects. An infected individual slowly becomes paralyzed and later on slip into a state of coma and die.
How rabies spreads
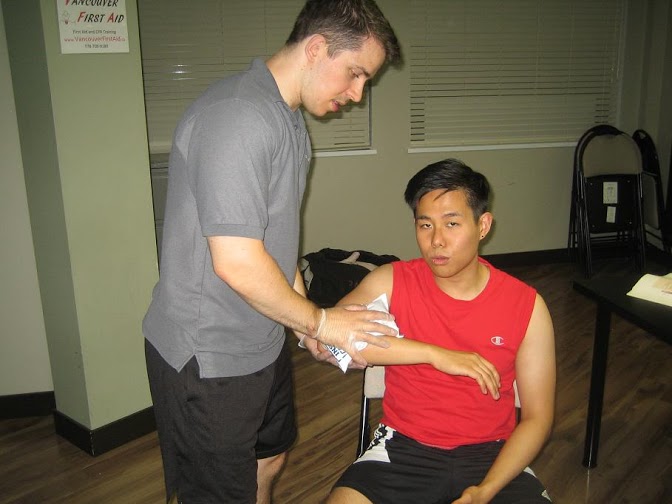
Animals who have been infected can transfer the virus to other animals and humans via saliva after a scratch or bite. Nevertheless, any exposure with the mucous membranes or an open wound can spread the virus. Among humans who acquire rabies, a nibble from a dog that was not vaccinated is the usual cause.
When an individual is bitten, the virus spreads via the nerves and up to the brain. If the bite is on the neck, it is vital to seek help as soon as possible.
After a bite, the virus spreads via the nerve cells up to the brain. Once the virus reaches the brain, it starts to multiply. This causes significant inflammation of the spinal cord and the brain after which the individual rapidly deteriorates and dies.
Who are at risk?
The risk for acquiring rabies is low but there are certain scenarios that might put one at higher risk such as the following:
- Living in an area populated by bats
- Living in a rural area where there is higher exposure to wild animals or limited access to vaccinations
- Travelling to developing countries
- Those below the age of 15
- Regularly camping and being exposed to wild animals
Even though most cases of rabies are caused by dogs globally, bats are the main cause of death due to rabies in some countries.