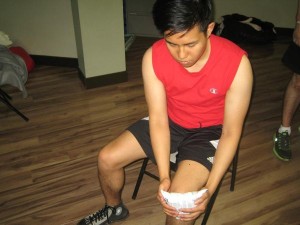
Chronic knee pain is defined as long-term pain, swelling or sensitivity in one or both knees. Various conditions can cause or contribute to chronic knee pain. Luckily, there are different treatment options available.
What are the causes?
It is important to note that chronic knee pain rarely settles without treatment. It is often the result of various conditions or causes.
Some of the physical conditions or diseases that trigger pain include:
- Osteoarthritis
- Bursitis
- Tendinitis
- Gout
- Chondromalacia patella
If bursitis is the cause, it can be managed with application of ice for 15 minutes every hour. - Baker’s cyst
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Meniscus tear
- Dislocation
- Torn ligament
- Bone tumors
What are the signs?
The signs of chronic knee pain tend to vary for every individual and the cause often affects how the pain feels.
If an individual has chronic knee pain, it can manifest as:
- Continuous ache
- Dull burning discomfort
- Shooting, sharp pain if the joint is used
In some cases, there is chronic swelling and pain if the knee is touched.
Management of chronic knee pain
Depending on the underlying cause of chronic knee pain, there is a specific treatment such as:
- Medications
- Physical therapy
- Injections
- Surgery
If bursitis is the cause, it can be managed with application of ice for 15 minutes every hour. It is also recommended to use well-cushioned, flat shoes that support the feet.
Outlook
In some cases of knee pain especially if due to osteoarthritis, it is likely to be permanent. Without any extensive form of treatment or surgery, the pain, swelling and inflammation in the knee can persist.
The long-term outlook for chronic knee pain involves pain control, prevention of flare-ups and reducing irritation on the knee.